These infections of the dentals are often considered as not so grave issues, but if ignored, they may quickly worsen to be severe in health terms. People often ask, how long until a tooth infection kills you? Not uncommonly, tooth infections would lead to death in most people, though it is rare. The reality is that an untreated dental infection can be fatal in just days or weeks. Knowing what may happen and seeking attention promptly are crucial elements in avoiding such severe outcomes.
But what is a tooth infection, really? And how does it turn fatal? These are important questions to be answered for the full understanding of the gravity behind this dental condition.
What is a Tooth Infection?
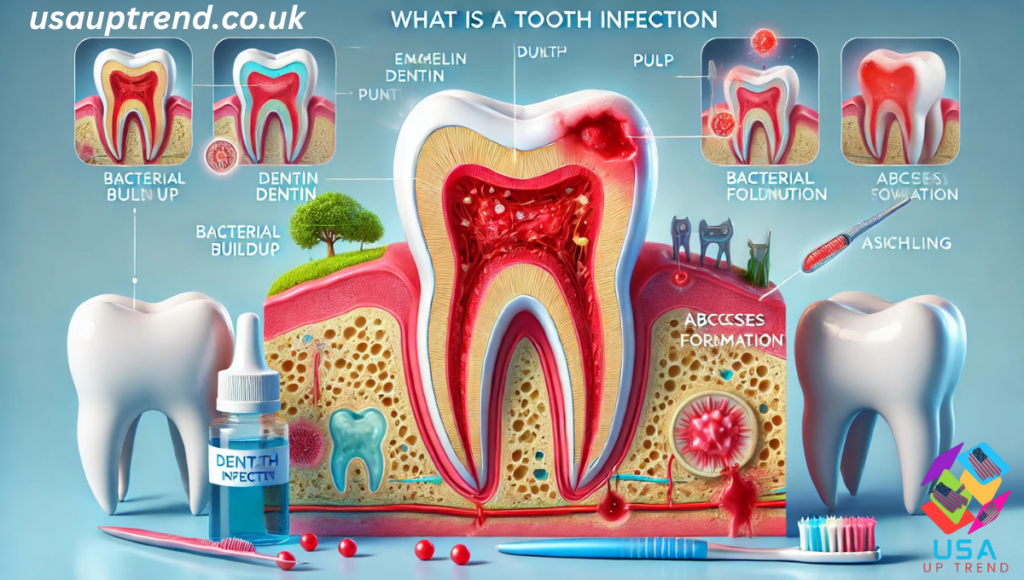
There is bacterial infection of the teeth and, in fact, an accumulation of pus brought on by an infection of the dental abscess. The infection may also be established at the root or between the gum and the tooth. Causes of tooth infections may include trauma, gum diseases, fractured teeth, or cavities not treated. Common symptoms include.
- Severe toothache
- Swelling in the face or jaw
- Red, swollen gums
- A bad taste in the mouth or bad breath
- A fever and a body ailment
When not treated immediately, an infection might travel into the different parts of your body, for instance, down into your jaw or neck and eventually to the blood. That time, your dental infection from a tooth has now become one of the causes that put your health in danger.
How Long Until a Tooth Infection Kills You?
It’s very hard to establish an exact timeline for this, but complications from a tooth infection can show up in a pretty short period of time. Extremely bad conditions such as sepsis can show up as early as a few days to a few weeks. The response to the question how long until a tooth infection kills you? This will greatly differ according to parameters like the general condition of the person, as well as the severity of the infection itself, in terms of its rate of spreading. Consider the following steps of which it should be illustrative for an untreated dental infection progression
1: Primary infection stage
The infection occurs strictly between the limits of the tooth and its adhering gum. There would probably be a degree of pain, redness, and sensitivity.
2. Secondary infection
It may begin infecting the tissues next to the infected area, and a skin infection caused by the bacteria called cellulitis or abscess within the jaw.
3. Systemic infection
Sepsis, a potentially fatal illness characterized by a systemic inflammatory reaction, may result if it gets into the bloodstream.
4. Organ failure and death
If medical treatment is delayed, sepsis may cause organ failure and septic shock, which can be fatal.
Tooth Infection Death Rate
Although rare, deaths from tooth infections still occur. Studies indicate that the death rate for tooth infections that become severe, causing complications like sepsis is between 10% and 40% depending on the severity and promptness of the treatment. Modern medicine has dramatically reduced these statistics from the historical rates, but the danger still exists for those who do not treat or delay the treatment.
The following are some notable factors that determine the death rate for tooth infections.
- Healthcare: Those areas with low access to dental and medical care are more prone to complications and deaths.
- Underlying Diseases: Individuals whose immunological systems have been compromised or who have any kind of immune disorder, like diabetes, often become more sensitive to severe infection.
- Age: Elderly and very young children are at higher risks of complications due to dental infections.
- Tardive therapy: Complications will worsen the longer treatment for a tooth infection is postponed.
Treatment for Tooth Infection
Tooth infections can be treated, especially if caught early. The following are a few typical treatment options.
- Antibiotics: To combat the bacterial infection, antibiotics are generally necessary to be given. It prevents further spread but has no effect on the dental cause.
- Pus removal: Pus needs to be removed after the training, thereby exerting pressure on the abscess-formed area.
- Root Canal Treatment: This treatment repairs the damaged tooth’s pulp, cleans it, and helps in making sure that the infection does not worsen. It normally works in keeping the damaged tooth intact.
- Extraction of Tooth: If the tooth is either highly damaged, then it is to be treated by extraction. This way if the infected tooth is removed then it would not spread the infection.
- Pain Management: When symptoms need to be controlled, the patient may be advised to take some over the counter pain relievers throughout therapy.
A dentist must be visited in case symptoms develop. For emergencies like swelling that cannot be treated as it will impact breathing, and fever that doesn’t subside, a patient must rush to a medical facility for prompt treatment.
Indications That a Tooth Infection Is Getting Dangerous
Comprehending the warning signs of a severe infection is essential. You must pursue emergency help if you come across any of these.
- Having trouble eating or breathing
- Rapid heart rate
- Severe swelling in the face, neck, or jaw
- High fever and chills
- Confusion or lethargy
- Persistent vomiting
These signs suggest that the infection has probably extended beyond the tooth and might necessitate hospitalization.
How to Prevent Dental Infections

In dental care, it is always better to prevent than cure. The mentioned procedure would decrease the chances of getting infected teeth.
- Oral hygiene: Good oral hygiene involves rinsing, brushing teeth twice a day, flossing, and killing microorganisms in the mouth.
- Dental checkup: Have cleaning and examination performed on your teeth once every two years.
- Avoid sugary foods: Sugary foods are one of the most common culprits behind cavity related infections.
- Treat Oral Problems as Soon as Possible: Never tolerate gum diseases, cavities, or chips. The sooner one addresses these problems; the less likely they are to lead to an infection.
- Be Protective: If you are into sports, a mouth guard is necessary to prevent your teeth from injury
Comparison Table: Common Tooth Infections and Risks
| Type of Tooth Infection | Symptoms | Potential Complications | Treatment Options |
| Dental Abscess | Severe pain, swelling, fever | Cellulitis, sepsis, jaw infection | Antibiotics, drainage, root canal |
| Periodontal Abscess | Gum swelling, bleeding | Tooth loss, bone infection | Deep cleaning, drainage |
| Periapical Abscess | Pain at tooth root, sensitivity | Bone loss, systemic infection | Root canal, antibiotics |
| Dry Socket (after tooth extraction) | Intense pain, bad breath | Delayed healing, infection | Pain relief, medicated dressing |
Final Thoughts about Tooth Infection Kills you
Tooth infections can never be considered lightly. Most infections are treatable, but neglecting dental treatment can be fatal. The title asking how long until a tooth Infection Kills You? emphasizes the significance of prompt action and recognition of risks.
If you believe you have a tooth infection, do not hesitate to obtain professional assistance. Early treatment and prevention will prevent severe complications in health. Remember that oral health is one of the main components of your total well-being and may save your life if prioritized.
Read more Articles about Health and other Categories at usauptrend.co.uk