Introduction to Motherboard USB 3.0 Header Y Split
Modern computer systems require proper usage of available ports and expansion options. USB connectivity can be maximize through a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split. This USB 3.0 header Y-splitter allows users to create two USB connectors. It uses one single USB 3.0 header on a motherboard. It increases the number of available USB ports. No additional expansion card or hub is needed. This article details the significance, uses, and installation of a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split. It also covers the technical aspects of its deployment.
What are USB 3.0 Headers on Motherboards?
You have to understand, first of all, what a USB 3.0 header is. On most modern motherboards, USB headers are internal connectors. They allow the motherboard to interface with front panel USB ports on the computer case. Specifically, USB 3.0 headers support the faster USB 3.0 standard. Boasting transfer rates of up to 5 Gbps. In comparison to the maximum rate of 480 Mbps offered by USB 2.0.
A standard motherboard will have one to three USB 3.0 headers. These connect the front panel USB ports. But with more and more use of external devices as storage devices. Peripherals and other accessories. There will always be a growing demand for more USB 3.0 ports. This might be beyond the number of USB 3.0 headers on a motherboard.
What is a Motherboard USB 3.0 Header Y Split?
It is a small cable or device. It splits one USB 3.0 header into two separate headers. This splitter converts one USB 3.0 header to two. Thus, in a system, a user may have more than double the number of available USB 3.0 connections.
This is ideal for people with a case containing more front panel USB ports than the motherboard supports. The case could also have extra USB ports for ancillary items. These include external hard drives, gaming peripherals, or other USB-powered accessories.
Advantages of Using a Motherboard USB 3.0 Header Y Split
Maximized USB connectivity Using a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split will maximize the availability of USB 3.0 ports. .A splitter can instantaneously double the number of ports. This is beneficial for a user who needs to link multiple high-speed USB connections.
Cost-Effective Option
Instead of purchasing additional expansion cards , you could purchase it for less than one-fifth of the cost of the other two options. It is inexpensive and installed easily, but with this, you do not have to spend too much more on other expensive hardware upgrades when you would want to upgrade the USB capabilities of your system.
Easy Installation
Installing a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y splitter is actually relatively straightforward and does not require advanced technical knowledge. The splitter is therefore made to directly connect to available USB 3.0 header on the motherboard; then, further connectors are placed to connect front-panel USB ports or other peripherals. This would make it an appealing DIY project or casual setup option for many users.
No Additional Power Source Is Needed
Unlike the case when connecting through a USB hub, the motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split has no need for an additional power source to function. They are directly powered from the motherboard’s USB 3.0 header. This offers means users can expand their options for USB connectivity without introducing excess power cables and other sources.
Technical Considerations and Limitations
Although a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split is convenient and generally very economical, here are some technical considerations you might want to pay attention to when installing one:
Shared Bandwidth
It splits the bandwidth available from one USB 3.0 header across two connections. This doubles up the number of USB ports that are available but means that the two ports share the 5 Gbps bandwidth offered by the single header. However, unless you will be using numerous devices that involve content that will consume more bandwidth than the average PC activity such as external hard drives at the same time, shared bandwidth probably will not cause any problems for most users.
Compatibility
Many modern motherboards do support USB 3.0 headers, but check to see which motherboard model is compatible with a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y splitter. Some older motherboards do not have a USB 3.0 header at all or use a different pin configuration that would conflict for its usage.
Cable Management
The use of a this motherboard brings more cables inside the case and could increase the challenges of cable management. It is essential to plan the installation to avoid clutter and to maintain the proper airflow inside the case.
Device Limitations
Even though the motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split doubles the available number of USB connections, Such a connection will double the connections available, but it does not increase the bandwidth or power available to each connected device.The users should be aware of the power their USB devices draw so as not to load the system disproportionately.
Installing a Motherboard USB 3.0 Header Y Split
Installing it is actually not that complicated. Most users can install a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split in just a couple of minutes by following these steps:
Turn off the Computer
Turn off your computer and unplugged for safety.

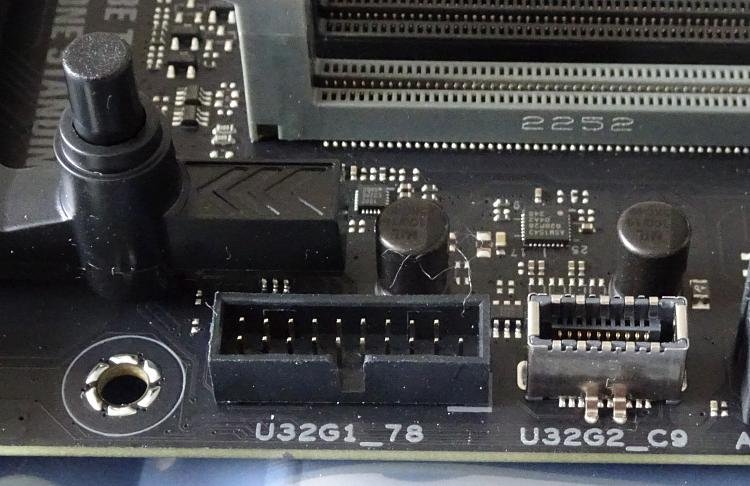
Locate the USB 3.0 Header
Open the computer case and locate the USB 3.0 header on the motherboard. It should typically be a 19-pin connector, which most motherboards have identified.
– Molière
Connect the Y Splitter
Mount the motherboard USB 3.0 header Y splitter to the USB 3.0 header on the motherboard. The splitter should fit tightly into the header without needing a special tool.
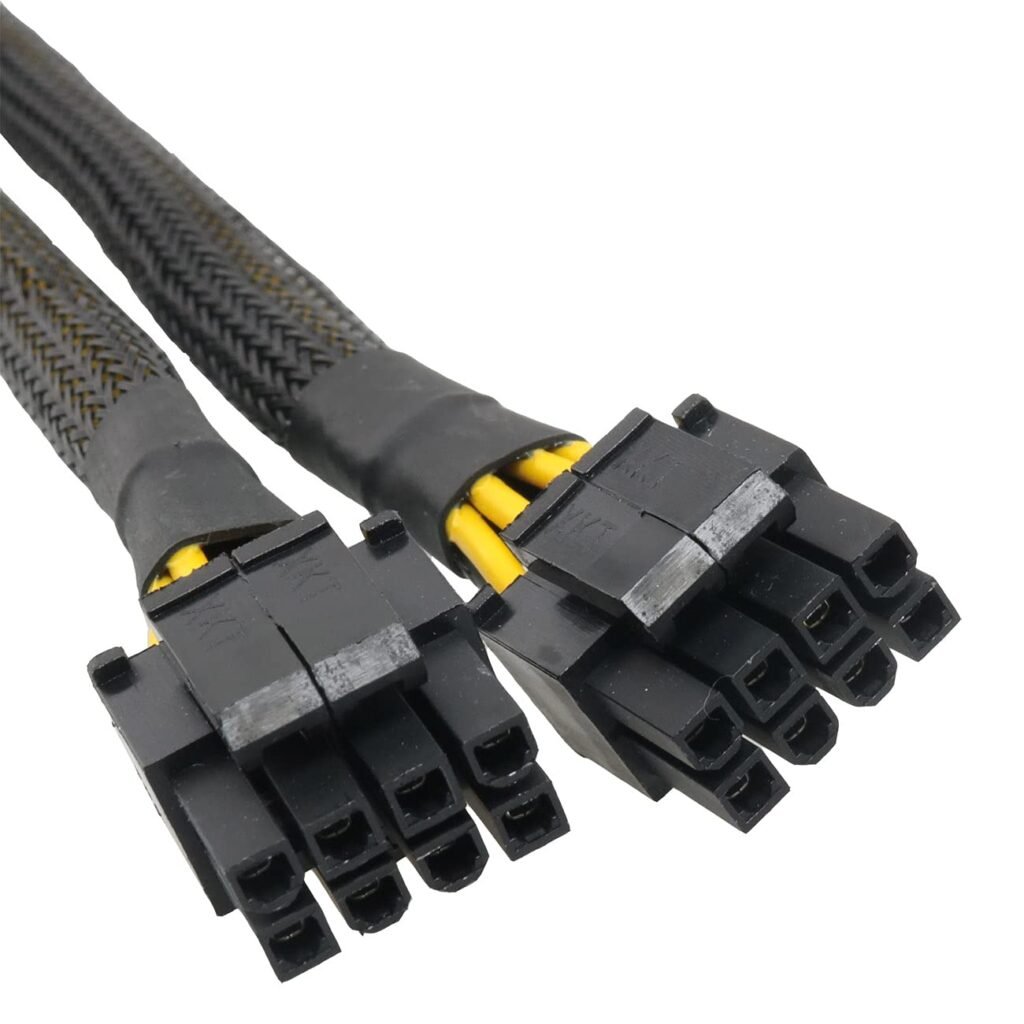


Connect USB Devices
Once you have installed the splitter, you should be able to connect your front panel USB ports or other USB devices to the additional connectors that the splitter has offered.the USB 3.0 Header
Close the Case and Power On
Once everything is installed, so turn on the system.

A comparison table between Motherboard USB 3.0 Header Y Split and other common solutions
| Feature | Motherboard USB 3.0 Header Y Split | Expansion Cards | External USB Hub |
| Functionality | Turns one USB 3.0 header into two, doubles USB connections | Adds additional USB ports via PCIe slot | Adds more USB ports by connecting externally via a USB port |
| Cost | Low-cost, typically under $10 | Moderate to high cost, typically $20-$50+ | Low to moderate cost, ranging from $10-$30 |
| Installation | Easy, connects directly to a motherboard USB 3.0 header | Moderate difficulty, requires opening the case and installing | Very easy, plug-and-play |
| Power Source | Powered by the motherboard’s USB header | Requires additional power (for high-end cards) | Some hubs require external power adapters |
| Port Expansion | Doubles the number of USB 3.0 ports using existing headers | Adds multiple USB 3.0 and sometimes USB 3.1 ports | Adds multiple USB 2.0/3.0 ports |
| Bandwidth | Shared bandwidth across split ports | Full bandwidth per port | Shared bandwidth across all connected devices |
| Cable Management | May add cable clutter inside the case | Cables grow internally according to the card’s ports | No need for internal cable management |
Conclusion
A motherboard USB 3.0 header Y split is one of the easiest and most efficient ways of expanding the number of USB 3.0 ports available to the system for connecting peripherals if users desire additional USB ports.
It is an inexpensive means of increasing the number of available USB ports without additional expansion cards. While there is some technical consideration that shared bandwidth as well as the usual cable management concerns, using a motherboard USB 3.0 header Y splitter is something of a no-brainer in any system where USB connectivity is a priority.
You Can Read more about it at Technology