A reaction involving both a metal and a nonmetal can either be a synthesis or decomposition. A combination of a metal with any nonmetal to create new compound is known as the synthesis. On the contrary, decomposition is breaking one compound into simpler substances. It is a majorly important concept in chemistry-metal and nonmetal synthesis or decomposition reaction. It highly helps in most industrial processes. If one understands these reactions, they would be able to know how common materials come into existence or break apart.
The ionic bond forms through a synthesis reaction, in which the metal transfers electrons to the nonmetal. Decomposition reactions are reactions that break up these ionic bonds into its separate components. This process is fundamental in making many compounds.
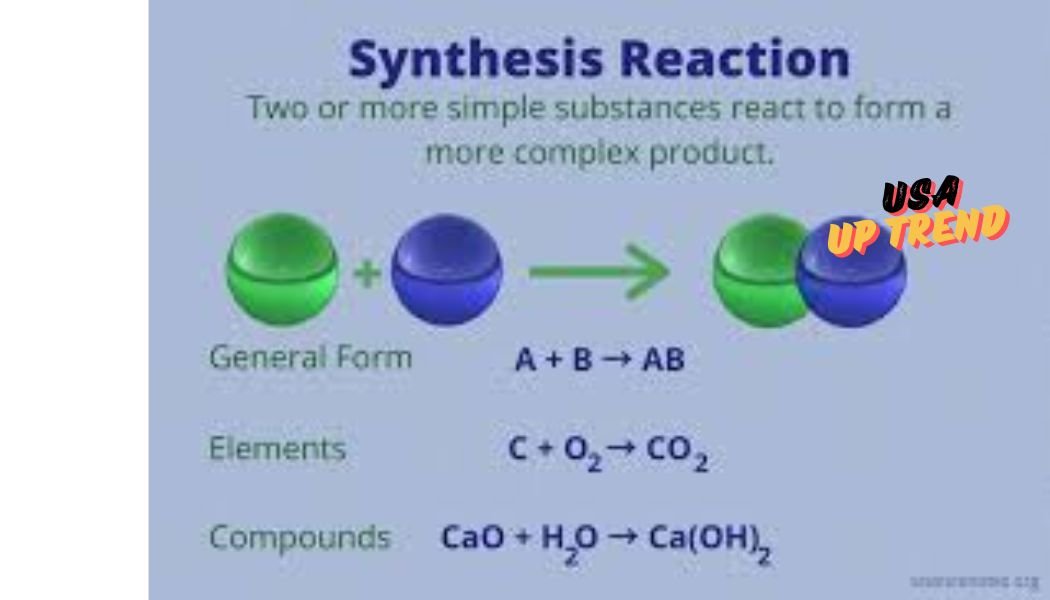
Is Synthesis a Reaction Between a Metal and Nonmetal?
Synthesis reactions are a third special type of chemical reaction in which two or more reactants combine to give only one product. Frequently, the result of this type of reaction involving a metal and a nonmetal is an ionic compound. For example, sodium when combined with chlorine forms sodium chloride, common table salt. In this case, sodium gives up one electron to become a positive ion, and chlorine acquires one electron to become a negative ion. The transfer of an electron describes the combination reactions of metals with nonmetals.
It plays an important role in several fields; for example, synthesis reactions in the area of pharmaceuticals can make compounds from simple elements and in the case of metals and nonmetals result in salts or some stable substances with actual usage. Synthesis reactions often take several factors such as temperature, pressure, and the catalytic presence that go in order to determine speed and efficiency at which reaction happens. In every case, it is the interaction of the electrons that determines the formation of the compounds.
What is a Reaction Between a Metal and a Nonmetal?
It’s mostly a reaction in which there is a transfer of electrons from the metal to the nonmetal. These compounds are stable as it tends to form ionic bonds by transferring electrons. As a matter of fact, the nature of metals is that they are electron losers while that of the nonmetals is to gain electrons. One of the most classic reactions is that between sodium and chlorine in which the sodium atom donates a chloride an electron to form sodium chloride.
Such reactions are the base of many ionic compounds formed, which are essential both in biological systems and in industrial processes. These reactions are frequently exothermic, involving the release of energy as heat. The stability of the resulting compound is contingent upon the strength of ionic bonds between the metal and nonmetal atoms. These reactions can be sensitive to extrinsic conditions, like temperature and pressure, altering their rate. The product from these reactions is therefore a unique compound, generally having properties different from the elements from which they were created.
What is a Synthesis Reaction Between a Metal and a Nonmetal Resulting in the Formation of an Insoluble Salt of Iron?
In some cases, the synthesis reaction of a metal and a nonmetal may result in forming an insoluble salt. Probably one of the best-known reactions is the reaction with iron, which is the metal, and the nonmetals sulfur or oxygen. The reaction of iron and sulfur produces iron sulfide (FeS), which forms an insoluble salt in normal conditions. Such compounds are of large significance in the synthesis reaction, especially in the metallurgical industries; their formation can either be beneficial or challenging under specific conditions.
The formation of insoluble salts, as in the case of iron sulfide, shows that their synthesis is an important application which requires knowledge of solubility. The metal combines with the nonmetal with a particular ratio in a synthesis reaction, and a compound’s properties depend strictly on the valence electrons of the involved elements. Salts, being insoluble, represent stable compounds that do not dissolve readily in water and therefore find use in applications that would include corrosion resistance or addition to industrial processes. Still, this insolubility poses some challenges in terms of waste management and sustainability of the environment, where such compounds are hard to break down or dispose of.
Synthesis or Decomposition Reactions What are they?
The simplest chemical reactions are synthesis and decomposition. Synthesis involves two or more reactants coming together to give one product. This is typically when a metal reacts with a nonmetal, thereby giving an ionic compound. Decomposition is the breakdown of a compound into simpler substances. These can either be elemental components or smaller compounds. A good example of decomposition is the reaction of calcium carbonate, CaCO₃ decomposing into calcium oxide, CaO and carbon dioxide, CO₂.
In synthesis and decomposition reactions involving metals and nonmetals, electrons are transferred.
. When synthesis occurs, the metal usually loses, but the nonmetal gains electrons to form an ionic bond. Decomposition breaks the bonds formed and frees the metal and nonmetal elements or compounds. The mechanisms of these reactions need to be understood wherever in material science to environmental chemistry, where compound formation or destruction can have useful applied consequences.
Examples of Reactions Between Metals and Nonmetals
| Reaction Type | Example with Metal and Nonmetal |
| Synthesis Reaction | Sodium (Na) reacts with chlorine (Cl₂) to form NaCl (table salt) |
| Decomposition Reaction | Silver chloride (AgCl) breaks down into silver (Ag) and chlorine gas (Cl₂) |
Conclusion
Chemical compounds have the reaction between two different elements. A metal reacting with a nonmetal to break or form through synthesis and decomposition. Such reactions demonstrate interactions and changes between elements in formation for new compounds or breaking to simpler substances. In synthetic reactions, electrons are exchanged when ionic compounds are usually stable, like sodium chloride. Decomposition reactions have the characteristic that ionic compounds breakable into their respective elements. Due to the breaking of one ionic compound, in this case, silver chloride.
The above reactions are crucial to understand in terms of both theoretical and practical uses. Synthesis reactions are widely used in industries for the formation of new materials. Whereas decomposition reactions have a vital role in the recycling and waste management process. The interaction between metals and nonmetals in these reactions indicates. The dynamic character of chemistry and its capacity to change matter in many different ways.
FAQS
What occurs in a reaction between a metal and a nonmetal?
A metal loses electrons to a nonmetal, producing an ionic bond, and a stable compound forms.
What is a synthesis reaction between a metal and a nonmetal?
A synthesis reaction occurs when a metal and a nonmetal react to form a new compound, usually an ionic one.
What is a decomposition reaction between a metal and a nonmetal?
In a decomposition reaction, a compound decomposes into simpler substances; separating the metal and the nonmetal.
Why are synthesis reactions between metals and nonmetals important?
These reactions form necessary compounds such as salts. Most of them are use industrially and in everyday life.
Can decomposition reactions reverse synthesis reactions?
Yes, decomposition reactions can, in many cases, undo synthesis by breaking the bonds that formed in synthesis.
What is a synthesis reaction between a metal and a nonmetal?
A very common example is sodium reacting with chlorine to form sodium chloride (table salt).
What is a decomposition reaction that contains a metal and a nonmetal?
A common example is silver chloride decomposing into silver and chlorine gas.
Are synthesis and decomposition reactions exothermic?
Synthesis reactions are commonly exothermic, which releases energy. Decomposition, however may require the application of energy.
How would temperature and pressure influence such reactions?
Temperature and pressure may affect synthesis and decomposition reactions. As they do have a tendency to change how fast and even if a given reaction would be.
What is different about ionic and covalent bonding in these reactions?
In metal and nonmetal reactions, ionic bonding occurs where metals lose electrons and nonmetals gain them. Covalent bonds are form by sharing electrons, usually between nonmetals.
Read more about Technology at USA UP TREND