Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from digital attacks. It protects sensitive information from unauthorized access. Cybersecurity ensures that online threats do not harm personal or business data.
Cybersecurity is so important today in this modern digital world. The reason is that cyberattacks are being developed rapidly, and most people should know how to prevent them from happening to themselves. For an individual and a business, Cybersecurity is always on top of their lists.
Cybersecurity encompasses network security, cloud protection, and data encryption. It helps prevent data breaches and keeps information secure. With advancing technology, the need for strong Cybersecurity measures is increasing.
What does cybersecurity actually do?
Cybersecurity is useful for a number of reasons, all of which relate to protecting data, systems, and networks from unauthorized access and potential damage. First, it prevents a breach. It creates barriers to prevent unauthorized users from accessing sensitive data through the development of strong firewalls, encryption protocols, and multi-factor authentication systems. This, therefore, protects a wide range of assets, such as cloud systems, local servers, and personal devices, such as smartphones and laptops.
The second role of cybersecurity is to identify breaches when such occur. With the best defense systems available, no organization or person is completely free from the risk of cyber threats. Once a breach occurs, networks are monitored by cybersecurity, which identifies unusual activity; thus, quick action can take place to limit the attack. Advanced detection systems, such as intrusion detection software and AI-based anomaly detection, can identify patterns that could signal a cyberattack and alert IT professionals to act right away. This is critical to prevent the widespread damage unchecked cyber threats can cause.
The 5 Areas of Cybersecurity
Cybersecurity is a broad area that encompasses many specialized fields, each addressing different aspects of protecting digital assets. There are five primary areas in cybersecurity:
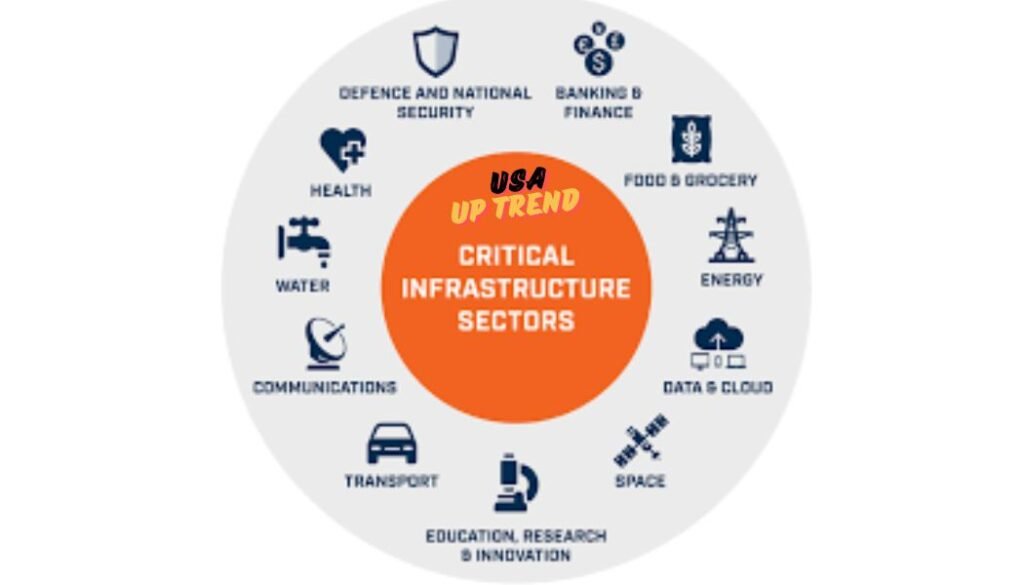
1. Critical Infrastructure Security
Critical infrastructure security is the protection of critical systems and networks vital for society’s operation, including power grids, water supply systems, and healthcare institutions. An attack on such systems would result in severe disruption, so it has become a high priority area for security measures. Such areas include industrial control systems and supervisory control and data acquisition, which are mostly weak in the modern world because of their age.
2. Network Security
Network security focuses on safeguarding an organization’s internal network from unauthorized access, misuse, or modification. This area uses firewalls, virtual private networks (VPNs), and encryption technologies to create secure communication channels. Network security is vital for preventing data breaches, ensuring the confidentiality of communications, and protecting sensitive information transmitted across networks.

3. Cloud Security
As more organizations move their operations to the cloud, cloud security has become increasingly important. Cloud security entails the set of technologies and policies designed to protect data, applications, and services hosted in cloud environments. These security measures prevent unauthorized access, data loss, and potential vulnerabilities caused by shared infrastructure in public or hybrid cloud systems.
4. Application Security
Application security ensures that software applications are developed and deployed securely, free from vulnerabilities that could be exploited by attackers. This area of cybersecurity includes practices like secure coding, application testing, and regular updates. Application security measures are essential for preventing data breaches and unauthorized access to the software.
5. Endpoint Security
With the rise of remote work, endpoint security has become a critical aspect of cybersecurity. Endpoint security protects individual devices, such as laptops, smartphones, and tablets, from being compromised. Through antivirus programs, anti-malware tools, and device encryption, endpoint security ensures that these access points do not serve as entryways for cybercriminals into larger networks.
Key Areas of Cybersecurity
| Area of Cybersecurity | Description |
| Critical Infrastructure Security | Focuses on protecting essential systems like power grids and water supply from cyberattacks that could cause havoc. |
| Network Security | Safeguards an organization’s internal networks using firewalls, VPNs, and encryption to prevent unauthorized access. |
| Cloud Security | Protects data and services hosted in cloud environments, addressing risks related to shared infrastructure. |
| Application Security | Ensures that software applications are free from vulnerabilities through secure development and testing practices. |
| Endpoint Security | Protects individual devices from being compromised by using antivirus programs, encryption, and anti-malware tools. |
The 7 Types of Cybersecurity
To fully understand the scope of cybersecurity, it’s important to recognize the seven main types of cybersecurity. Each type addresses a specific set of risks and vulnerabilities, and together, they provide a comprehensive security solution.
1. Network Security
As mentioned earlier, network security focuses on preventing unauthorized access to and from a network. It involves firewalls, VPNs, and encryption techniques that ensure data is transmitted securely between devices.
2. Information Security
Information security, also known as data security, protects sensitive information from unauthorized access, use, disclosure, or destruction. This type of cybersecurity emphasizes the importance of protecting data through encryption, backup procedures, and secure storage.
3. Operational Security
Operational security (OPSEC) deals with managing and protecting data as it is processed and used within an organization. It involves procedures for accessing and sharing data safely and implementing strict access controls that limit who can view and modify sensitive information.
4. Cloud Security
Cloud security protects online data that is stored in cloud services like AWS, Microsoft Azure, and Google Cloud. As organizations increasingly move their operations to the cloud, cloud security becomes essential to prevent unauthorized access to sensitive data.
5. Application Security
This area focuses on ensuring that applications are secure by design. Developers use secure coding practices, application vulnerability testing, and regular patch updates to protect against exploits and malware attacks targeting software applications.
6. Disaster Recovery and Business Continuity
This aspect of cybersecurity involves preparing for potential cyberattacks and ensuring that an organization can recover quickly and resume operations. Disaster recovery plans ensure that critical data is backed up and that systems can be restored in the event of an attack.
7. Identity Management and Access Control
Identity management ensures that only authorized individuals have access to certain data and systems. Multi-factor authentication (MFA), biometric systems, and role-based access controls are commonly used to ensure that sensitive information is only accessible to the right people.
Is Cybersecurity High Paying?
Cybersecurity is one of the fastest-growing fields, with high demand for skilled professionals. As organizations face an increasing number of cyberattacks, the need for cybersecurity experts has skyrocketed, making it a lucrative career path. According to industry data, cybersecurity professionals, including security analysts, consultants, and engineers, can expect high salaries due to the specialized skills and knowledge required for the job.
Entry-level positions in cybersecurity, such as information security analysts, can start with competitive salaries ranging from $70,000 to $90,000 annually. With experience and additional certifications, professionals can earn significantly more, with roles such as cybersecurity engineers and chief information security officers (CISOs) earning upwards of $150,000 to $300,000 annually. The high demand for cybersecurity professionals, coupled with the increasing sophistication of cyber threats, ensures that this field will continue to be financially rewarding for those with the right expertise.
Moreover, many cybersecurity roles offer opportunities for remote work, adding flexibility to an already attractive profession. Whether working for government agencies, private corporations, or as independent consultants, cybersecurity experts have a wide range of opportunities to explore. As cyberattacks grow more complex, businesses and organizations are willing to invest heavily in cybersecurity to protect their assets, making it a highly rewarding and stable career choice.
Conclusion
In conclusion, cybersecurity is a multi-layered and essential field that plays a critical role in protecting digital infrastructures from an ever-increasing range of cyber threats. By focusing on the key areas such as network security, cloud security, and application security, and understanding the types of cybersecurity measures, businesses and individuals can better prepare themselves against potential attacks. Moreover, the field’s high-paying nature makes it an attractive career option for those looking to specialize in this vital area of technology.
Cybersecurity will continue to evolve, adapting to the new threats and challenges posed by advancing technology. Staying informed and implementing robust security measures will ensure that digital environments remain safe and secure for all.
FAQs
1. What is Cybersecurity?
Cybersecurity is the practice of protecting systems, networks, and data from cyber threats, such as hacking, phishing, and malware attacks. It involves various technologies and practices to keep sensitive information safe from unauthorized access.
Why is important?
Cybersecurity is crucial because it protects personal and business data from being stolen, damaged, or manipulated by cybercriminals. With the increasing number of online threats, strong cybersecurity measures help ensure privacy and the integrity of digital systems.
What are the common types of threats?
Common threats include phishing attacks, malware, ransomware, and social engineering. These threats aim to steal data, cause system damage, or hold systems and data hostage for ransom.
4. Who needs Cybersecurity?
Everyone who uses the internet needs cybersecurity, from individuals protecting personal data to businesses safeguarding sensitive customer information. Government agencies, corporations, and small businesses all require cybersecurity to protect their systems.
5. What are some basic steps to improve Cybersecurity?
Basic steps include using strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, regularly updating software, avoiding suspicious emails and links, and installing antivirus software. These steps reduce the risk of cyberattacks.
6. What are the 5 areas of Cybersecurity?
The five key areas of cybersecurity are critical infrastructure security, network security, cloud security, application security, and endpoint security. Each area focuses on protecting different parts of a digital ecosystem.
7. What are the 7 types of Cybersecurity?
The seven types of cybersecurity include network security, information security, operational security, cloud security, application security, disaster recovery, and identity management. These focus on different security aspects within organizations.
Read more about Technology at USA UP TREND